
A Thermoelectric Power Plant (TPP) is a power generation unit that uses heat as its primary source, capable of encompassing different methods such as coal, natural gas, or biomass. Currently, the biggest challenge for TPPs is to minimize CO₂ emissions and use renewable raw materials in their operation.
Thermoelectric power plants play a major role in energy supply in Brazil. In 2024, this type represented 22.77% of the country’s power plants, ranking second only to Hydroelectric Plants (49.02%) and ahead of Wind Power (15.75%).
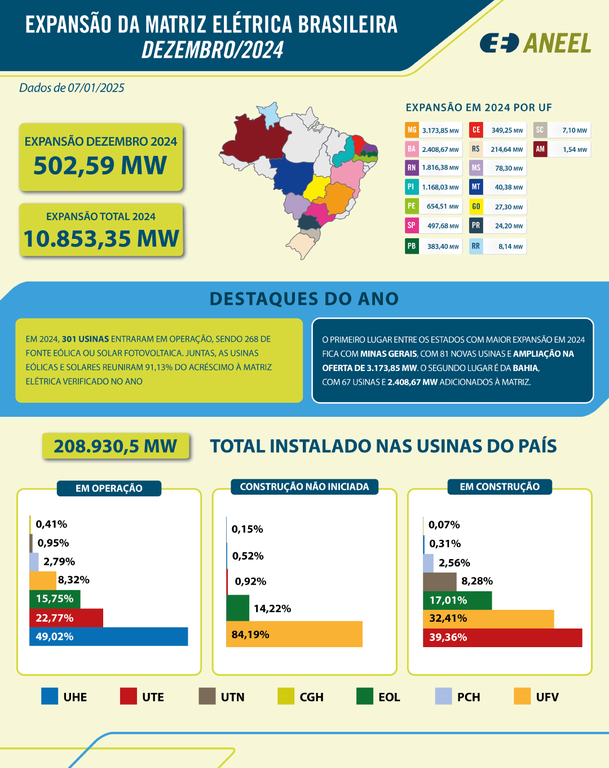
Source: Aneel
How energy is generated in a TPP
Thermoelectric energy is the transformation of thermal energy (heat) into electricity, usually through a combustion process using:
- Coal or natural gas – traditional sources, still widely used in some countries.
- Fuel oil or diesel – used in smaller or emergency power plants.
- Biomass – agricultural waste, wood, organic residues.
- Municipal Solid Waste (Waste-to-Energy, WtE) – treated and incinerated waste used for power generation.
The heat generated in this process is used to heat a boiler with water, producing high-pressure steam that converts heat into mechanical energy to drive a turbine coupled to a power generator. The generator then produces high-voltage alternating current (AC).
After passing through the turbine, the steam loses pressure and is directed to a condenser to be cooled down, return to its liquid state (water), and be pumped back into the boiler, restarting the cycle.
From the generator, the energy leaves at voltages ranging from 10 to 25 kV. Step-up transformers increase this voltage to 69 kV, 138 kV, or even 500 kV, reducing transmission losses.
The energy then flows through transmission lines to substations, where the voltage is stepped down for residential, commercial, and industrial consumption.
Thermoelectric power and renewable energy
Although thermoelectric energy is not considered renewable due to its dependence on fossil fuels, more and more renewable supply solutions are being implemented, such as the use of biomass or the generation of electricity through the combustion of biogas produced from the controlled decomposition of waste.
In São Paulo, Orizon VR, a company specialized in waste recovery, installed the Paulínia Verde Thermoelectric Plant, which uses biogas and biomethane to convert thermal energy into electricity.
Committed to the energy transition through renewable sources, Orizon demonstrates that it is possible to create alternatives to non-renewable thermoelectric energy, using renewable sources that also address other contemporary issues such as inadequate solid waste management.
In 2024, Orizon acquired two additional biogas-powered TPPs — one in Pernambuco and another in Paraíba — and is also dedicated to building the Energy Recovery Unit in Barueri, in the metropolitan region of São Paulo.
Thermoelectric Energy from Biogas
Thermoelectric Energy from Biogas is produced through the anaerobic decomposition of solid waste, which generates gases that are captured and purified, then sent to a combustion system where engines are activated to generate electricity.
A biogas plant is directly connected to the municipal power grid, and the generated energy can be traded on the energy market.
Thermoelectric Energy from Waste-to-Energy
The energy generated in a Waste-to-Energy (WtE) Unit comes from the combustion of non-recyclable solid waste.
The heat produced by combustion heats a boiler, transforming water into high-pressure steam, which drives the plant’s turbines to generate electricity.
The future of thermoelectric energy
In line with the global goal of energy transition to fight climate change, thermoelectric energy is undergoing a transformation that will enable the replacement of fossil fuels with renewable sources.
New plants using combined gas and steam cycles may achieve 20% to 30% higher efficiency than conventional thermal power plants. These new processes can not only ensure low-carbon energy but also generate carbon credits, supporting the energy transition in other sectors.
The future of thermoelectric energy will bring security to the power system by using renewable raw materials such as solid waste.
Orizon is a company that works daily to implement solid waste recovery, integrating its solutions into the creation of renewable and efficient energy.



